Type 1 Diabetes [f9d5ec]
Type 1 Diabetes [f9d5ec]
Post Time: 2025-07-29
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for our overall well-being. But what exactly are normal blood sugar levels? The ideal range varies from person to person, but generally, it's considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dL after an overnight fast of at least eight hours. However, this can vary depending on the individual's age, medical history, and other factors.
For example, for adults under 50 years old with no underlying health conditions, a blood sugar level of less than 100 mg/dL is considered normal. But what happens when our blood sugar levels start to rise? Fluctuations in blood sugar can lead to a range of problems, from mild symptoms like fatigue and irritability to more severe issues such as cardiovascular disease.
The Role of Diet in Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Did you know that the foods we eat have a significant impact on our blood sugar levels? A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods can help regulate blood sugar. On the other hand, consuming high-carbohydrate and high-sugar foods can lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose.
For instance, a study found that eating breakfast cereal with added sugars caused an average increase of 32 mg/dL in blood glucose levels within one hour after consumption. In contrast, complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are digested slowly, preventing sudden surges in blood sugar.
The Impact of Exercise on Blood Sugar Levels
Regular physical activity can also help regulate blood sugar levels. When we exercise, our body becomes more sensitive to insulin, allowing glucose to enter the cells more efficiently. Even mild exercises like walking or yoga have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and lower HbA1c levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
In fact, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that exercising for at least 150 minutes per week reduced the risk of developing insulin resistance by up to 40%.
Managing Stress to Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Stress is another significant factor influencing blood sugar levels. When we experience stress, our body releases cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood glucose levels even if we're eating healthily.
Interestingly, research has shown that meditation and other mindfulness practices can reduce the impact of chronic stress on blood sugar regulation. For example, a study found that regular practice of yoga reduced HbA1c levels by an average 2% in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The Connection Between Sleep and Blood Sugar Regulation
Lastly, adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. During sleep, our body repairs itself, regulates hormones, and even helps to control inflammation – all of which can affect blood glucose levels.
Did you know that sleeping less than six hours a night has been linked to an increased risk of developing insulin resistance? On the other hand, research suggests that getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night can help regulate appetite hormones like leptin and ghrelin, leading to improved weight management and blood sugar control.
Common Misconceptions About Blood Sugar Regulation
One final point worth mentioning is common misconceptions about managing blood sugar levels. For instance, many people believe that consuming simple carbohydrates during exercise will improve performance – but this can actually lead to energy crashes later on.
To avoid these pitfalls, focus on whole foods, regular physical activity, stress management techniques like meditation or yoga, and a balanced sleep routine. By incorporating these habits into your daily life, you'll be well on your way to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels for optimal health!
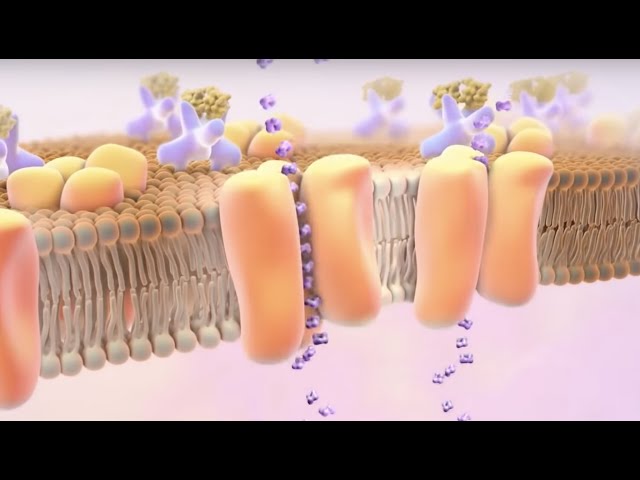
#Type1Diabetes #insulin #BloodSugar MEDICAL ANIMATION TRANSCRIPT: You or someone may have been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. This video will help you understand what it is and why it's important to keep it under control. Type 1 diabetes is a condition where your pancreas makes little or no insulin. Insulin is a chemical your body needs to keep your blood sugar at a normal level. Carbohydrates are substances your body uses to make energy. After you eat food that contains carbohydrates, it eventually goes to your small intestine. In your small intestine, the food is broken down into single sugar molecules called glucose. The cells in your small intestine soak up the sugars, which pass into your bloodstream. When the blood reaches your pancreas, it detects the high amount of sugar in your blood. Normally, this causes your pancreas to put a chemical called insulin into your bloodstream. The insulin reduces the amount of sugar in your blood to a healthy level. statins and blood sugar levels How does insulin do this? As the blood moves through your body, the insulin and sugar exit the bloodstream into your tissues to reach your cells. Most cells have structures on their surfaces called insulin receptors. When insulin flows blood sugar 300 by, it attaches to the receptor. The insulin acts like a key in a lock to open up the cell so the sugar can get inside. Now your cell can use the sugar to make the energy it needs to work properly, and your blood sugar level drops back to its normal range. If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas loses its ability to make enough or any insulin. This can result in high blood sugar levels and other complications. In type 1 diabetes, your immune system attacks some cells in your pancreas by mistake. As a result, your pancreas makes little or no insulin. Without insulin, sugar cannot get into your cells. Without sugar, your cells don't have energy. And since the sugar is locked out of your cells, it builds up to a high level in your bloodstream. This is a condition called hyperglycemia, which can lead to serious complications. If you have questions about type 1 diabetes or any medications you have been prescribed, speak with your doctor. It is important to take your medications as directed by your doctor. Tell him or her about any side effects you have. ANH16174 146 blood sugar